comprators
Introduction
- If four people take a measurement with the same instrument,it is for sure that there will be discrepancies in their readings.
- Hence precision measurements with consistent accuracy, the human element should be completely eliminated This is achieved by using instruments called comparators
Classification of comparators :
- Depending on the method by which the difference in dimensions is magnified,the comparators are classified as
- 1.mechanical
- 2.electrical
- 3.optical
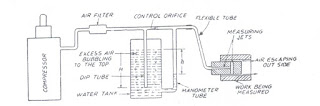
- 4.pneumatic
- In general,mechanical comparators are limited to the lower magnification
- Pneumatic comparators are the most accurate type in their operation
Use of comparator
- Comparator is an indirect type of instrument with the help of which an unknown dimension of a work piece is compared with a working standard (usually slip gauges)
- Micro-comparator is one of the instruments used for checking various gauges in the industry.
- It ensures that the wear effects do not allow the gauge dimensions to fall outside the prescribed limits .
Principle of operation of a comparator
- The basic principle of operation of a comparator is that the comparator is first adjusted to zero on its dial or recording device with a gauge block in position
- The gauge block is of dimension,which the work piece should have.
- Then you must place the work piece to be checked in position and use the comparator to check its dimension.
- The dimension of the work piece may be less than, equal to or greater than the standard dimension
- If the dimension is less or greater than the standard,the difference will be shown on the dial or the recording device of the comparator
- Thus ,a comparator does not give the dimension of a work piece,but only gives the difference between the standard and the actual dimension of the work piece
- In comparators , this difference is shown as magnified on the dial or the recording device
- If a comparator has a magnification of 1000 and if the difference between the standard and actual dimensions of a work piece is 0.02mm it will result in pointer movement of 20mm on the dial or the recording device of the comparator
Accuracy of a comparator
- The absolute accuracy of a comparator is guaranteed by use of standard slip gauges, slip gauges employed for setting working gauges are themselves checked by micro-comparator for wear effects
- For very accurate and for absolute results light wave interference method is used.
- The indirect method of testing gauges consists in using two comparators where relative difference from standard size is obtained
- Comparators are available up to the accuracy of 75 millionth of an mm.



Comments
Post a Comment